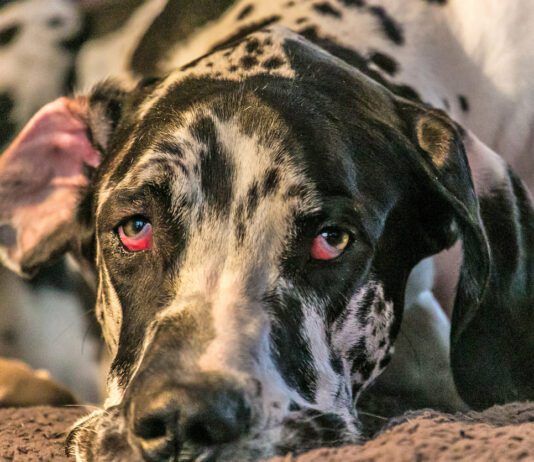
Canine Bladder Infections
If you've lived your life with dogs, chances are you've cared for one with a bladder infection. The normal urinary bladder is sterile, meaning devoid of bacteria. Infection occurs when bacteria find their way into the bladder and set up housekeeping. Bacterial cystitis (medical-speak for a bladder infection) is a common diagnosis in the canine world. The term urinary tract infection (UTI) is often used synonymously with bacterial cystitis. Technically speaking, a UTI can mean infection anywhere within the urinary tract, and is not specific to the bladder.
Vaccine Titer Tests for Dogs
or if your adult dog really needs any more core vaccines.
Identifying Tumors on Your Dog
anyway. In this case
Advice for Tick Removal
Is it my imagination, or is a plague of ticks currently in effect? Everywhere I go with my dogs these days, they come back crawling with ticks. I use Frontline on them, though I've used Advantix in the past as well as apple cider vinegar rinses and essential oil sprays and Skin-So-Soft wipedowns. For whatever reason, Frontline seems to work better than anything else on my dogs, in my area, though I hear contrary reports from other dog owners in other places. I'm seriously considering making a line of Tyvek canine coveralls, instead.
New Hope for Treating Osteosarcoma On the Horizon
Many dogs do just fine after amputation necessitated by osteosarcoma. A new vaccine may help them continue to enjoy life even longer.
April 2014 Letters & Corrections
Correction: In the list of WDJ-approved dry foods presented in our February issue, we reported incorrect ranges for the amounts of protein and fat in some of the dry foods made by Dogswell. The products in the company's Live Free dry food line contain 36% to 40% protein and 14% to 18% fat. The products in Dogswell's dry Nutrisca line contain 30% to 32% protein and 16% to 18% fat. We regret the errors.
How to Properly Examine Your Dog
because Otto wasn't growling or trying to get away. He would benefit from some counter-conditioning.üThis dog loves being petted but panics when being even gently restrained. He would benefit from some counter-conditioning, so he forms the same sort of positive association he has with being petted as he does with being held or restrained.üThis dog is uncomfortable with being touched on the head. The handler is feeding her a treat that she likes, but you can tell the dog's backward-leaning posture and tightly tucked tail that the proximity of the petting hand and the handler's body has the dog obviously over her threshold for comfort.üThat's better! When the handler leans back a bit, and feeds the treat with her hand near, but not on the dog's head, the dog relaxes a bit. Her tail is still tucked, though, telling us she is near her threshold.
Preventing and Treating Kennel Cough
You're not likely to forget it if you've heard it even once: the half-cough, half-choke sort of like a Canada goose in need of a Ricola lozenge that signals your dog has come down with kennel cough.
How & Why You Should Manage Your Dog’s Dental Hygiene
The good news: you can give your dog a thorough brush job in just two minutes a day. The bad news: few dogs fancy having their teeth brushed, and there ain't no Holy Grail of Canine Tooth Brushing, despite my attempts to extract one from Angela Mees, DVM, who owns a practice limited to veterinary dentistry in suburban Atlanta.
Keeping Your Dog Thin is a Lifesaver
but he looks and acts much older. He's at high risk of a short
Home Treatment for Parvo May Prevent “Economic Euthanasia”
When experienced breeder Barbara Sorg noticed that Winks, one of her five 8-week-old puppies, was listless, not eating, and by nightfall was suffering from diarrhea, she hustled him off to her long-time veterinarian the next morning, a Tuesday.??The vet suspected that Winks had not tolerated the dewormer he'd been given Sunday. Although he had never left her property and had no suspected exposure, Sorg asked that he be tested for deadly parvovirus; her veterinarian discounted the possibility.
Use Caution When Filling Veterinary Prescriptions at Human Pharmacies
A few years ago, I was at my vet’s office when an older couple brought in a Chihuahua puppy who was very ill. Despite the staff’s best efforts, less than an hour later the pup was dead. The cause? A drug overdose, due to a prescription error made by a human pharmacy.