Commercial Dog Food For Allergies
Owners who don't feel capable of or willing to carry out a rigorous trial may prefer to try a commercial dog food that has been processed in such a way as to render the proteins hypoallergenic, or one designed specifically for use in an elimination diet. Chances are good that your veterinarian carries at least one of these types of food. Some are limited-ingredient diets, available over the counter; others are prescription diets. All cost around 30 percent more than even the best nonprescription dog foods.
10 Steps to Healthy Skin and a Silky Coat for Your Dog
All dog lovers appreciate seeing a healthy, happy dog, running in the sun with a glistening coat. And it's great to hear, Wow! Your dog's coat is so soft and shiny. How do you do it?" It's wonderful if you are one of the lucky owners whose dog inspires this sort of spontaneous compliment
Behavior Medication Opens Doors
After about six weeks of living with Trill, Dr. Sharp knew that the frightened, anxious dog needed something more. The training and behavior protocols were working in the sense that the dog was cooperative, but Trill still had a panicked look in her eyes much of the time. Sharp was concerned: No animal should have to live with that much fear, she thought.
How to Tell If Your Dog Has Hip Dysplasia
My six-month-old Rottweiler has a goofy, bouncy walk. Does that mean she has hip dysplasia?A lot of puppies especially big, gangly ones have a clumsy, bumbling gait, and this does not mean they have hip dysplasia. If your puppy had a hip dysplasia, you might notice that she limps sometimes, especially after strenuous exercise. You might hear or feel her hips click in and out, or notice that she stands and walks with her hocks or hind feet very close together. You might notice her struggling to push herself up into a standing position when shes lying down, or she might have trouble climbing stairs.
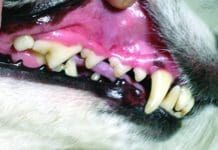
Save Your Dog’s Teeth with Home Care
Cooper, my service-dog-in-training, trotted briskly at the side of my power wheelchair as we headed to the veterinary clinic, a mile from home. He was overdue for a routine dental cleaning, and my regular veterinary clinic was not within rolling distance. I decided to take a chance on a new vet, since it was just a standard dental cleaning. I dropped him off and rolled back home, relieved that I was finally able to afford the procedure.
What To Do If Your Dog Has Worms
Deworming agents are present in any number of prescription and over-the-counter treatments for dogs and puppies. If your dog shows signs of a gastrointestinal worm infestation, there are all sorts of products available that are made exclusively to rid dogs of various types of worms. But there are also deworming agents included whether they are needed or not in many flea and tick treatments and in most heartworm preventive drugs; in fact, it's sometimes hard to find a minimalist flea treatment or heartworm preventive drug that does not contain dewormers. The question is, is this really necessary? Are intestinal parasites that much of an ongoing threat to most dogs and their owners?
October 2014 Letters & Corrections
I just finished reading my June issue of WDJ and, as usual, loved it! I just have one comment/question regarding Vaccine Titer Tests" where you state
Your Dog & The “Placebo Effect”
Most people are familiar with the concept of a placebo effect
Ways to Combat Your Dog’s Indoor Urine-Marking
I can still remember the day, more than a decade ago, when I first realized with horror that our Scottish Terrier, Dubhy (pronounced Duffy")
5 Things To Do If Your Dog Needs Cage Rest
Few things are worse than hearing the vet say those dreaded words: Cage Rest." Most often the consequence of an injury or major surgery
Neutering Dogs Without a Scalpel
such as humping
Tryptophan for Dogs
The tryptophan/turkey theory became so popular and widespread in the early 1980s that nutrient-supplement companies decided to bypass the turkey part of the equation altogether and began producing and selling tryptophan supplements (L-tryptophan). These were initially promoted as sleep aids and to reduce signs of anxiety. However, as is the nature of these things, the promoted benefits of L-tryptophan rapidly expanded to include, among other things, claims that it would enhance athletic performance, cure facial pain, prevent premenstrual syndrome, and enhance attention in children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. (My personal favorite was the promotion of L-tryptophan as a treatment for Tourette syndrome.)