LAMENESS IN DOGS: OVERVIEW
1. If your dog is limping, bring him to your veterinarian to determine the cause. Chances are your dog has a cruciate injury.
2. Keep a dog with a ligament injury quiet and confined.
3. Understand the risks and benefits of knee surgery for dogs so you can make an informed decision about which direction to take.
4. Explore physical therapy and other treatments that strengthen joints.
5. No matter the treatment, speed your dog’s recovery with nutrition, physical therapy, and other support.
Why is My Dog Limping?
Dogs go lame for all kinds of reasons. Arthritis, Lyme disease, paw injuries, muscle sprains, bee stings, interdigital dermatitis, and dislocated kneecaps can make any dog limp. But when an active dog suddenly can’t put weight on a hind leg, the most common diagnosis – for more than a million American dogs every year – is a torn cruciate ligament. In 2003, according to the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, cruciate ligament dog surgery costs exceeded $1.32 billion, and the price tag keeps rising.
The most common prescription for dog knee injuries is surgery. Unfortunately, operations don’t always work and some patients, because of age or other conditions, are not good candidates. In recent years a nonsurgical approach called “conservative management” has helped thousands of dogs recover from ligament injuries, and it is growing in popularity. At the same time, conservative management is not a cure-all. It doesn’t always prevent the need for surgery, it is not necessarily less expensive, and it can require as much time and effort as post-surgical rehabilitation. At its best, conservative management improves the outcome of whatever treatment is needed for full recovery.
“Conservative management consists of any nonsurgical treatment of injuries,” says Faith Rubenstein, who founded an online forum devoted to the subject in 2004, “including physical therapy, chiropractic adjustments, acupuncture, massage, nutrition, the use of a leg brace, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, medicinal herbs, prolotherapy, weight loss for overweight dogs, and other noninvasive treatments.”
Rubenstein, who now lives in Austin, Texas, first encountered dog CCL injuries when her 100-pound Briard, Dakota, then six years old, experienced a partial tear of his cranial (anterior) cruciate ligament. “When our veterinarian recommended that we see an orthopedic surgeon,” she says, “I went looking for answers.” An academic researcher who is now a private investigator, Rubenstein discovered the term “conservative management” in a veterinary textbook.
The orthopedic surgeon diagnosed a partial tear in both of Dakota’s knees and recommended immediate TPLO (tibial plateau leveling osteotomy) surgery. In this procedure, the tibia is cut, then rotated and held in place with a metal plate and screws so that after the broken bone heals, weight-bearing exercise stabilizes the knee joint.
“I had misgivings about this method,” she says, “especially because surgeons at the School of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania don’t use it. I spoke with Gail Smith, the head of the University’s department of clinical research, and with Amy Kapatkin, a board-certified orthopedic surgeon who was then at Penn. What Dr. Kapatkin said made perfect sense to me. She asked, ‘Why break a bone to fix a ligament?’ My whole interest in conservative management was triggered by my fear of the TPLO.”
The University referred Rubenstein to an orthopedic surgeon who used other methods. He found Dakota to have so few symptoms that he agreed to write a prescription for physical therapy in hopes that it might make surgery of any kind unnecessary.
“Physical therapy and exercise made all the difference,” she says. “Dakota never needed surgery, and neither did his littermate, Aubrey, who tore his cruciate ligament a few months later. Many veterinarians believe that the only effective treatment for these injuries is surgery – either TPLO or another surgery – but that simply isn’t true. Conservative management is a TPLO surgery alternative that can help most patients, including those who eventually have surgery, and then recover to lead active, happy lives.”
Understanding Ligament Injuries in Dogs
The stifle (knee) connects the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (leg bone) with a patella (kneecap) in front and fabella (a small bean-shaped bone) behind. Cartilage (the medial meniscus and lateral meniscus) cushions the bones, and ligaments hold everything in position.
Two key ligaments, the anterior (front) and posterior (back) cruciate ligaments, cross inside the knee joint. In animals, these ligaments are called cranial and caudal, respectively. The anterior or cranial cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from slipping out of position.
Veterinarians see most ligament patients immediately after their injuries, when symptoms are acute, or weeks or months later, after symptoms become chronic. If not immediately treated, most ligament injuries appear to improve but the knee remains swollen and abnormal wear between bones and meniscal cartilage creates degenerative changes that result in osteophytes (bone spurs), chronic pain, loss of motion, and arthritis. In some patients, osteophytes appear within one to three weeks of a ligament injury. Swelling on the inside of the knee, called a “medial buttress,” indicates the development of arthritis in patients with old injuries.
The main diagnostic tools for ligament injuries are X-rays, which can rule out bone cancer as a cause of leg pain, and a procedure called the “drawer test,” in which the veterinarian holds the femur with one hand and manipulates the tibia with the other. If the tibia can be moved forward, resembling a drawer being opened, the cruciate ligament has been torn or ruptured.
The drawer test is not necessarily conclusive because the tense muscles of a frightened or apprehensive dog can stabilize the knee temporarily. To produce more accurate results in such cases, patients may be sedated before being tested.
In the tibial compression test, which is another way to check for ligament damage, the femur is held steady with one hand while the other flexes the dog’s ankle. A ruptured ligament allows the tibia to move abnormally forward.
“A completely torn CCL in dogs is always a surgical case,” says Stacey Hershman, DVM, of Hastings-on-Hudson, New York, “since otherwise the knee cannot function as a hinge joint.” Advocates of conservative management recommend that whenever the tear is partial, nonsurgical techniques be given an eight-week try. If symptoms improve during that time, they say, the odds favor ACL recovery without surgery. If symptoms don’t improve, conservative management techniques can be used as pre- and post-operative conditioning and therapy.
Which Dogs Are at Highest Risk for Leg Injury?
Any dog can injure a cruciate ligament, but large breeds are most susceptible. According to one study, Neapolitan Mastiffs, Newfoundlands, Akitas, Saint Bernards, Rottweilers, Chesapeake Bay Retrievers, and American Staffordshire Terriers lead the list. Most veterinary clinics have seen ligament injuries in Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherd Dogs, and other popular large breeds.
Young, athletic dogs playing hard can turn or step the wrong way and suddenly not be able to walk. Cruciate ligament injuries are unfortunately common in dogs who compete in agility, obedience, field trials, and other active sports.
Some veterinarians report progressive lameness in young Labrador Retrievers, Rottweilers, and other large-breed dogs resulting from a partial rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament. This may not be associated with a specific injury but may instead result from poor stifle biomechanics combined with a yet-to-be-defined conformation abnormality.
Older large-breed dogs can develop weakened ligaments that eventually tear, especially in dogs who are overweight. When a weakened ligament is stressed, its rupture can be triggered by activities that are otherwise insignificant, like sitting on cue, stepping over a curb, or jumping off a sofa.
A small dog’s size may not prevent a ligament injury, but smaller dogs usually recover faster. One study that compared dogs six months after their cruciate ligament ruptures found that 85 percent of those weighing less than 30 pounds had regained near normal or improved function while only 19 percent of those weighing more than 30 pounds had regained near normal function. Dogs in both groups needed at least six months to show maximum improvement.
Helping Your Dog After An Injury
If your dog is injured, visit your vet as soon as possible, but be an informed consumer. Many veterinarians consider cruciate ligament surgery necessary, routine, fast, easy, highly effective, and the only treatment that will help. For many dogs this has been the case, but some veterinary research places the cruciate ligament surgery for dogs success rate at well below 50 percent. If surgery is necessary, your investment in conservative management may pay dividends in faster recovery and better overall health.
Canine health and nutrition researcher Mary Straus recommends simple first-aid strategies for dogs with knee injuries. Straus learned about the benefits of such an approach when her dog, Piglet, had surgery for dysplasia on both elbows before her second birthday, followed by surgery for a ruptured cruciate at age three. “First and most importantly,” she says, “exercise must be restricted. No running, no jumping (including on and off furniture), and no stairs. Walk your dog on-leash when going outside to potty. The dog doesn’t necessarily have to be crated, which can restrict movement so much that it increases stiffness and limits flexibility, but should be confined to a small room or ex-pen, or kept on-leash while with the owner. Exercise restriction must be continued for at least six to eight weeks.”
Second, inflammation needs to be controlled. “I would use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs),” she says. “Inflammation contributes to cartilage degeneration and accelerates the development of arthritis. Don’t avoid NSAIDs in the hope that pain will keep your dog from overusing the leg. There are natural anti-inflammatories like bromelain, boswellia, quercitin, and turmeric, and I would use those as well, but they may not be strong enough alone. You could use white willow bark, which is comparable to aspirin, but it should not be combined with other NSAIDs. In addition to anti-inflammatories, I would give glucosamine-type supplements to try to protect the cartilage and slow arthritic changes. It’s questionable how much these help with cruciate injuries, but they do no harm and I would include them.”
Dr. Hershman prescribes Glycoflex, a nutritional supplement that contains freeze-dried Perna canaliculus or New Zealand Green Lipped Mussel. This product is recommended for joint and connective tissue support, for geriatric and working dogs, and as a follow-up to orthopedic surgery.
In addition, she gives subcutaneous Adequan® injections or teaches the owners to do so at home. Adequan Canine (polysulfated glycosaminoglycan) is a prescription, water-based, intramuscular, polysulfated glycosaminoglycan that helps prevent cartilage in the dog’s joint from wearing away. “I give injections twice a week for two weeks,” says Dr. Hershman, “then once a week for maintenance.”
She also recommends Wholistic Canine Complete Joint Mobility, which is a powder containing organic vitamins, minerals, digestive enzymes, hydrolized whitefish, immune-support ingredients, and pharmaceutical-grade glucosamine, chondroitin and MSM (methyl sulfonyl methane), all of which support healing, speed tissue repair, or help alleviate pain and inflammation.

Standard Process products for improved ligament health include Ligaplex, which contains organic raw bone, herbs, and minerals, and the veterinary product Canine Musculoskeletal Support, which contains anti-inflammatory herbs, Perna canaliculus, and whole-food ingredients that enhance tissue regeneration and improve joint health.
It is important to keep injured dogs from gaining weight, which can easily happen when their exercise routine is interrupted. “Overweight dogs have a harder time recovering from a cruciate ligament injury,” says Straus, “and they are more at risk for injuring the other knee. I would feed a high-protein, low-carbohydrate, reduced-fat diet. Fat is high in calories and so should be limited, but too little fat will leave the dog feeling hungry all the time. Protein helps with wound healing and also to create and preserve lean muscle, while carbs are more likely to be stored as fat. For those who feed kibble, I would cut back on the amount fed and add fresh, high-protein foods such as eggs, meat, and dairy. For seriously overweight dogs, this is one situation where I might consider using the drug Slentrol to help speed weight loss.”
Physical Therapy for Injured Dogs
Faith Rubenstein’s Dakota received physical therapy from Carol Wasmucky, PT, a licensed physical therapist for humans in Herndon, Virginia, who founded Pet Rehab Inc. and works full-time with animals by referral from veterinarians throughout Northern Virginia.
She began Dakota’s treatment by measuring his hind legs, one of which had atrophied and was smaller than the other. “Our goal,” says Rubenstein, “was to have both legs measure the same. Dakota and I worked with a holistic veterinarian, who put him on nutritional and herbal supplements, and we did acupuncture as well. I restricted his activity so he was not allowed to run off-leash for six months, and during that time he had regular physical therapy. Dakota wasn’t a swimming dog but he became one, for swimming was the perfect exercise for him. After six months, both hind legs were the same 17 inches in girth. He was in great shape, his drawer test results improved to nearly normal, and he didn’t need surgery.”
Dogs who are intermittently lame with a partial tear of the cruciate ligament are ideal physical therapy patients, says Wasmucky. In addition to providing weekly or twice-a-week ultrasound, laser, and electrical stimulation treatments, she puts patients on a home strengthening program with range-of-motion and stretching exercises. “Every program is different depending on the dog’s condition,” she says. “The owners are involved every day; I show them what to do. It’s just like working with human injuries; if you want the best results, you have to do your homework.”
Wasmucky, who has worked with thousands of canine patients over the past 10 years, encourages anyone whose dog has a partial tear to use physical therapy to build muscle so that even if surgery has to be performed, the dog goes in and comes out in better shape. “This means shorter rehab time,” she says, “and a faster recovery.”
Swimming is such effective exercise for injured dogs that many veterinary clinics have installed swimming pools. “Dogs who can’t yet do weight-bearing exercises can start in a pool,” she says, “and as they get stronger, they’re able to progress through the exercise program. I check their progress in weekly appointments and make adjustments as needed. It takes time to heal from ligament injuries and I like to be sure that dogs are completely well before they resume agility or other demanding sports.”
She requires a major commitment from owners. “It’s usually an hour or so every day in twice-a-day sessions,” she says, “and this can go on for months. It’s a big investment of time and energy, and it requires a motivated dog as well as a motivated owner, but it can make a world of difference in mobility and overall health.” For more about canine rehabilitation, see “The Benefits of Canine Rehab & Conditioning,” September 2009.
Prolotherapy for Dogs
Although most veterinary experts agree that there is no way to repair a damaged ligament, one alternative therapy claims to do exactly that. Prolotherapy, also known as proliferative or sclerosing therapy, has been used for over 30 years to treat musculoskeletal pain in humans, including arthritis, sports injuries, and damaged or partially torn ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
The term “prolo” is short for proliferation, as this treatment is said to cause the proliferation (growth or formation) of new tissue in weakened areas. Ligaments have a limited blood supply, which slows healing, but in prolotherapy, injections of dextrose (sugar water) or other benign substances cause localized inflammation that increases the supply of blood and nutrients, stimulating tissue repair.
Health columnist Jane E. Brody described prolotherapy as “injections to kick-start tissue repair” in the August 7, 2007 New York Times, where she wrote that most scientifically designed controlled studies of prolotherapy have shown “a significant improvement in the patients’ level of pain and ability to move the painful joint.” In studies of human knee injuries, she said, patients with ligament laxity and instability experienced a tightening of those ligaments, including the anterior cruciate ligament (also known as the ACL). Other studies showed a significant improvement in the symptoms of arthritis in the knee one to three years after prolotherapy injections.
In Royal Oak, Michigan, John Simon, DVM, uses prolotherapy to repair damaged cruciate ligaments in dogs. He explains, “Prolotherapy is a way of tightening up loose, unstable, hyper-mobile joints by injecting a ‘sclerosing’ agent in and around the joint. The resulting thickening of the joint capsule and the ligaments surrounding it act like scar tissue and eventually contract with time. The thickening and contraction of the ligaments and joint capsule increase joint stability and relieve joint pain.”
Most canine cruciate ligament patients receive five sessions at three-week intervals. “Although I tell caregivers not to expect any positive results until at least the third treatment,” he says, “I am occasionally surprised to see improvement after just one. Other modalities that I often recommend in conjunction with prolotherapy are soft laser therapy and pulse magnetic therapy. These treatments reduce pain and help the joint recuperate.”
According to Dr. Simon, the best candidates for prolotherapy ligament repair are dogs whose injuries do not involve torn meniscal cartilage in the joint. During the past three years, he has treated 35 dogs for cruciate ligament problems and estimates that 80 percent experienced significant improvement.
Getting Your Dog A Leg Brace
Debbie Kazsimer, who lives in Pennsylvania, knows a lot about cruciate ligaments. Trouble, her Shepherd/Husky mix, had TPLO surgeries at ages six and seven, and her Shepherd/Malamute mix, Fly, had a TPLO when she was two.
In 2005, the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association published the case of a German Shepherd Dog who developed bone cancer after her implant corroded. Two years later, Trouble was diagnosed with osteosarcoma, and when his leg was amputated, its metal implant was found to be corroded. The biopsy report linked the cancer to his 2004 TPLO surgery.
As a precaution, Kazsimer had Fly’s implant removed. “But by then five years had passed and it was too late,” she says. “The damage was already done.” Within months, both dogs died of osteosarcoma.
Four weeks after Fly’s death, Kazsimer’s six-year-old 100-pound Shiloh Shepherd, Kimber, tore a cruciate ligament. By then, Kazsimer had learned about conservative management and knew she didn’t want to put another dog through a TPLO surgery. Because of her experiences with Fly and Trouble, she was familiar with range-of-motion and physical therapy exercises, and she studied massage with her husband, Ken, an Integrated Touch Therapy canine massage therapist. She spent an hour or two daily on Kimber’s rehabilitation.
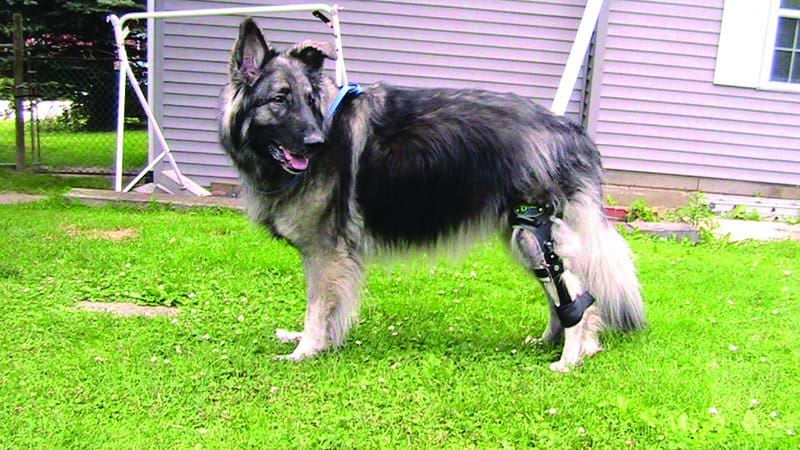
“I thought a leg brace would be a big help to her,” she says, “but my veterinarian refused to fit her for one because he was convinced it wouldn’t work. So my husband and son helped me to cast her leg with a casting kit from Orthopets. The brace supports the knee externally, just as surgery supports it internally.”
Kimber went from walking on three legs to walking on four, then swimming, then finally bearing full weight on her leg. Eight months after her injury, Kimber’s regimen of supplements, physical therapy, massage, swimming, and wearing the brace have enabled her to recover well without surgery. “She runs around like a wild girl!” says Kazsimer, who has posted videos of Kimber online, where you can see her running, swimming, and playing with and without her brace on. “It’s wonderful,” she says. “Kimber is able to do everything she did before she got hurt.”
Holistic Therapies and Home Treatment for a Dog’s Torn ACL
The most popular “hands-on” treatments for injured dogs include acupuncture, acupressure, chiropractic, and massage.
Dr. Hershman, a certified veterinary acupuncturist, treats patients with acupuncture to alleviate pain and enhance healing of the torn ligament. “I do this once or twice per week for the first two weeks,” she says, “depending on the dog’s level of pain, then once a week for five to six weeks, then once every two weeks, and finally once a month. When the dog is weight-bearing and in less pain, I stop.” Dr. Hershman is also a certified veterinary homeopath who prescribes homeopathic remedies according to the patient’s symptoms.
In the article “Post-op Acupressure” (August 2006), Nancy Zidonis and Amy Snow describe how stimulating specific acupressure points with a thumb or fingertip can help with pain management, clear the effects of anesthesia, minimize the building of scar tissue, and reduce swelling. Acupressure can be learned at home and applied whenever needed.
Veterinary chiropractors help speed the healing of injuries and surgeries by making adjustments that improve skeletal alignment and musculoskeletal function. (See “Chiropractors for Canines,” March 2008.) Chiropractic adjustments help restore normal nerve activity by gently moving bones, ligaments, and tendons back into alignment, and when ligaments are injured, adjustments help realign the body to improve balance and speed healing.
Canine massage therapists used to be unusual, but now they play an important role in maintaining and improving our dogs’ health. Efflurage, passive touch, kneading techniques, and stroking increase circulation, release muscle tension, reduce pain and soreness, relieve stress, and accelerate the repair process. Massage books and how-to videos make it easy for caregivers to apply these same techniques at home.
Online Support for Injured Dogs
Thanks to the Internet, anyone whose dog suffers a cruciate ligament injury can find a wealth of information about canine anatomy, surgical options, and alternatives to cruciate ligament dog surgery online.
The conservative management forum that Faith Rubenstein founded five years ago now has more than 2,000 members around the world. Paola Ferraris, who lives in Italy, is one of its moderators. “What I would like to stress is that conservative management is not an easy (and often not cheap) alternative to surgery,” says Ferraris. “Successful conservative management requires just as much commitment as post-op care. It’s tough love and careful management. Your work is basically the same as rehabbing a dog who has had surgery; in fact, a number of our members have had surgery done on their dogs and use the list for pre-op and post-op support.”
When her own dog suffered an ACL injury, Ferraris had to make decisions with little information. “The best way to discuss treatment with your veterinarian is when you understand the available options and their pros and cons,” she says. “I had to educate myself by spending nights doing research online, after the fact. I would have appreciated having more available information, which is what we now offer.”
Co-moderator Ansley Newton of Pownal, Maine, became interested in conservative management when her chocolate Lab, Dooley, injured his second knee. “The first knee had TPLO surgery,” she says, “so I was excited to try conservative management with the second knee.
Unfortunately after four months he did not get better and I chose to have a traditional surgery, which was very successful for this 90-pound dog. Then one day my large chocolate Lab, Nutmeg, came inside with that familiar limp. I again decided to try conservative management along with a knee brace, acupuncture, massage, swimming, and some other supportive techniques. Within six months she was back to normal with very little arthritis.
“After three ligament injuries, I thought I was done. But no, two years later Nutmeg came in limping again. I again went the conservative management route and things were going fine until the second month when Nutmeg had an oops moment. She was limping again, so I decided to do surgery but had to postpone it for a couple of months because I tore my own anterior cruciate ligament and damaged my meniscus at the same time!
“So here I was running a farm by myself on crutches and wearing a knee brace with a dog in a knee brace. What a sight we both were. I wish I had taken a picture. We were forced to stay with conservative management because there was no one to take care of the farm and I couldn’t drive Nutmeg to get her surgery. We limped through several months together and lo and behold, we both healed. Nutmeg was good to go in six months and it took me closer to 10. Nutmeg recently passed away from lymphoma. She was 14 years old and despite those two ligament injuries, her legs were still fine.”
The Surgical Options for Torn ACLs in Dogs
While it is not possible to repair canine ligaments surgically, lateral suture stabilization, or LSS techniques, can stabilize knee joints so that they function well.
In the extracapsular repair procedure, tom or partially torn ligament tissue and bone spurs are removed along with the damaged portion of the meniscus. Through a hole drilled in the front of the tibia, a large, strong suture is passed around the fabella behind the knee, which tightens the joint and replaces the cruciate ligament.
The intracapsular repair method, which is no longer popular in the United States but still widely used in the United Kingdom, replaces the cruciate ligament with a strip of connective tissue after the damaged meniscus and ligament fragments are removed. This “new ligament” is sewn into place or attached to an implant.
A ligament repair technique called the Tightrope procedure utilizes a fiber tape suture material developed for human ankle and shoulder reconstruction. This material
replaces the damaged cruciate ligament and stabilizes the stifle joint.
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy, or TPLO surgery, involves breaking and resetting the tibia. The meniscus cartilage is removed and, if badly damaged, the remains of the cruciate ligament may be removed as well. The repositioned bone is held in place with a metal plate and screws. This procedure treats an estimated 50 percent of all cruciate ligament injuries in the US. and its popularity helped double the number of American veterinary surgeons in a single decade (1995-2005). TPLO surgery requires a specialist and typically costs twice as much as extracapsular repair.
Tibial Tuberosity Advancement, or TTA, which was developed in 2002 at the University of Zurich, repositions the top of the tibia by separating and then anchoring it with titanium or steel implants. Like TPLO surgery, TTA requires special equipment and expertise.
None of these procedures work for every patient and all carry risks associated with the use of general anesthetics, post-operative infections, and other complications. The TPLO and TTA are most expensive and most invasive.
Which surgical method is best? Every procedure has its advocates and many veterinary surgeons claim high success rates, but the results of research studies can be sobering. In
2005, the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association published a study* comparing the results of lateral suture stabilization (LSS), intracapsular stabilization (ICS),
and TPLO surgery on 131 Labrador Retrievers with ruptured cranial cruciate ligaments and injury to the medial meniscus. Limb function was measured before surgery and again two and six months after. Treated dogs were also compared to 17 clinically normal Labrador Retrievers. Compared with the clinically normal dogs, only 14.9 percent of the LSS-treated dogs, 15 percent of ICS-treated dogs, and 10.9 percent of TPLO-treated dogs had normal limb function. Overall improvement was seen in only 15 percent of dogs treated with ICS, 34 percent of those treated with TPLO, and 40 percent of those treated with LSS.
* “Effect of surgical technique on limb function after surgery for rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament in dogs,” by Michael G. Conzemius, DVM, PhD, DVACS, et al. Journal of
the American Veterinary Medical Association, January 15, 2005, Vol. 226, No. 2, p. 232-236.
CJ Puotinen is a long-time contributor to WDJ and author of The Encyclopedia of Natural Pet Care and Natural Remedies for Dogs and Cats.